생태학, R/K 선택 이론, R/K selection theory, R/K strategists, K생물, R생물
생태학에서 r/K 선택 이론(r/K selection theory, r/K strategists)은 자손의 양과 질 사이에서 균형을 이루는 유기체의 특성 조합 선택과 관련이 있다. r- 전략은 개별 부모 투자를 분산하여 자손의 수를 늘리고, K- 전략은 부모 투자를 집중시키면서 자손의 수를 줄이는 것에 초점을 맞추는 것이다. 이 방법은 매우 다양하며, 겉보기에는 특정 환경에서 성공을 촉진하는 것처럼 보이다. 자손의 양 또는 질에 대한 개념은 때때로 "싼" 또는 "비싼"이라고 하며, 자손의 소모성 및 부모의 헌신에 대한 설명이다. 환경의 안정성은 소모성 자손이 많이 만들어지는지 또는 고품질의 자손이 적을수록 번식 성공률이 높아지는지를 예측할 수 있다. 불안정한 환경은 부모가 많은 자손을 낳도록 부추길 것이다. 왜냐하면 그들 모두(또는 대다수)가 성인이 될 때까지 생존할 가능성은 희박하기 때문이다. 대조적으로, 보다 안정적인 환경에서는 부모가 한 자녀에게 자신 있게 투자할 수 있다. 자녀가 성인이 될 때까지 생존할 가능성이 더 높기 때문이다.
r/K 선택이라는 용어는 1967년 생태학자 Robert MacArthur와 윌슨이 섬 생물지리학에 대한 연구를 바탕으로 만든 용어이다. 그러나 생명사 전략의 진화(evolution of life history strategies)라는 개념은 더 긴 역사를 가지고 있다.
이 이론은 1970년대와 1980년대에 휴리스틱 장치로 사용되면서 유행했지만 여러 실증적 연구에서 비판을 받으며 1990년대 초반에 그 중요성을 잃었다. 생활사 패러다임은 r/K 선택 패러다임을 대체했지만 중요한 주제를 생활사 이론의 하위 집합으로 계속 통합한다. 일부과학자들은 이제 각각 r 대 K 생식 전략을 대체하기 위해 빠른 수명 대 느린 수명(fast/slow life history)이라는 용어를 사용하는 것을 선호한다.

R/K selection theory
The terms r-selection and K-selection are used by ecologists to describe the growth and reproduction strategies of organisms
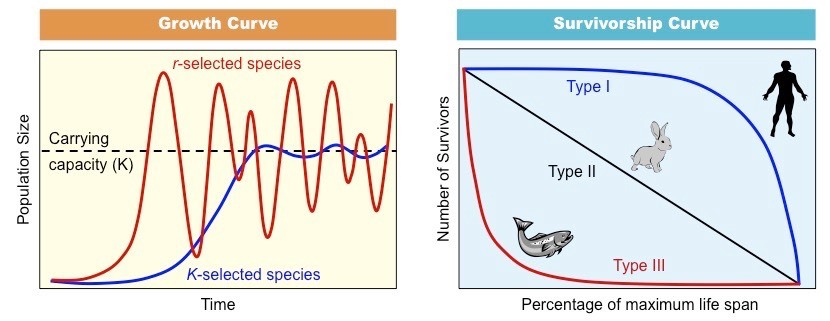
- r-selected species have a high growth rate but low survivability (“cheap” offspring)
- K-selected species have a low growth rate but high survivability (“expensive” offspring)
r-selection
- Occurs in unstable environments where there are ecological disruptions and resources are used for maximising reproduction
- There are usually many offspring per brood, which require little parental care and have a high rate of mortality
- The body size of offspring is typically small and they have an early onset of maturity (short developmental span)
- Population size is typically variable (highly fluctuating) and an example of a r-selected organism is a pioneer species
K-selection
- Predominates in stable or predictable environments where resources are used for maximising long-term survival
- There are usually very few offspring per brood, each requiring high levels of parental care (resulting in low mortality)
- The body size of offspring is typically larger and they have a late onset of maturity (long developmental span)
- Population size is typically stable (reaches carrying capacity) and an example of K-selection is a climax species
It can be difficult to determine if a species is following a r-strategy or a K-strategy as they represent two ends of an extreme
- In reality, most organisms typically demonstrate an intermediate strategy somewhere along the spectrum (e.g. type II growth)
- Some species may even change their selection strategy according to environmental conditions
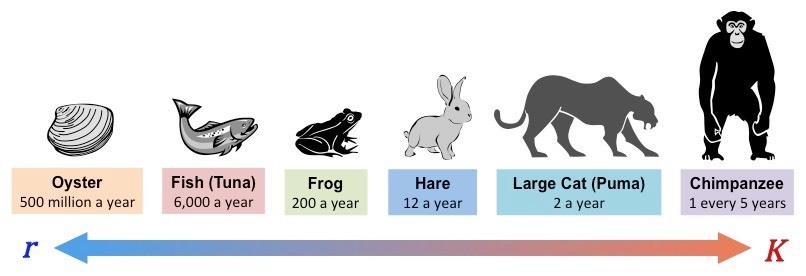
The r-K Scale of Reproductive Strategy: Offspring Numbers

Comparison of r-K Strategies: Growth Rate and Survivorship