

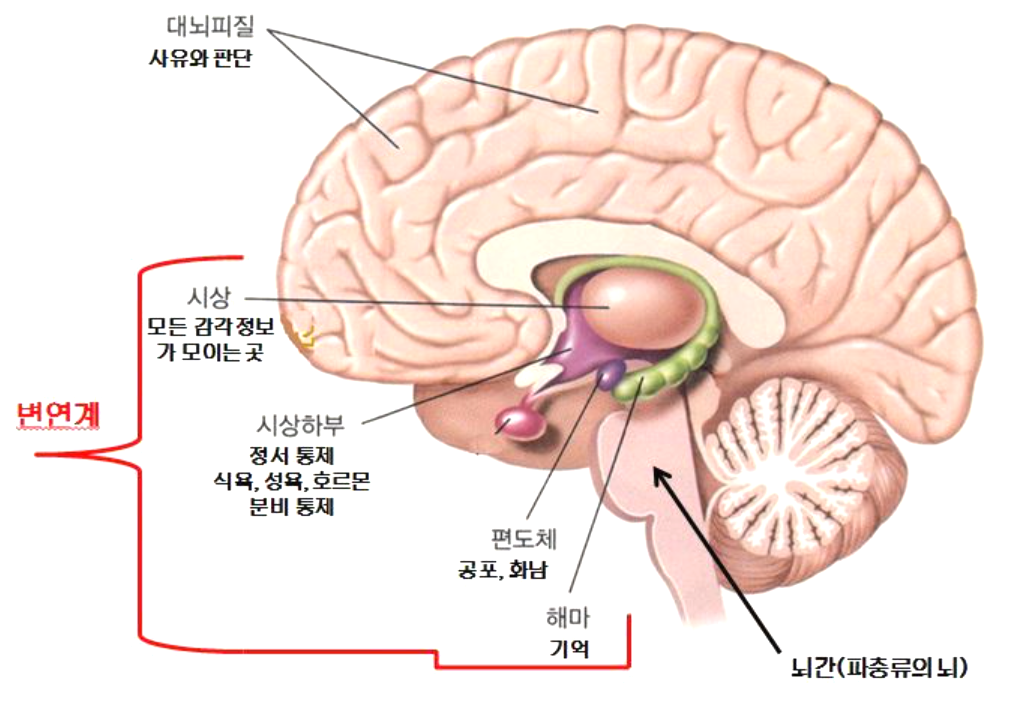
변연계 (Limbic System)
변연계(邊緣系)라는 말은 라틴어로 경계를 뜻한다. 이것을 한자어인 변연계로 변환했다. 경계를 뜻하는 변(邊)과 연결을 뜻하는 연(緣)이 이어진 말이 변연(邊緣)이다. 여기에 조직 혹은 체계를 뜻하는 계(系)가 이어져 최종 변연계라는 말이 생겼다. 따라서 변연계라는 두 개의 서로 다른 기관을 연결하는 두뇌의 기관이라는 말이 된다.
뇌간 (Brain Stem) 와 대뇌 피질 (Cerebral Cortex) 사이에 있는 신경세포의 집단으로 구성되어 있다. 2 억년에서 3 억년 전에 진화되었다. 이 변연계는 포유동물에서 가장 잘 발달되어 있기 때문에 종종 "포유동물 뇌" 라고도 불린다. 체온, 혈압, 심박동, 혈당을 조절하는 기능 외에도 생존에 관계되는 감정작용에 관여한다. 개체 및 종족유지에 필요한 본능적 욕구와 직접 관계가 있으므로 ‘본능의 자리’라고도 한다. 시상하부와 밀접하게 연결이 되어서 시상하부가 받아들인 충동이 여기서 통합된다. 즉, 간뇌 시상하부의 기능을 지배하고 있다고 생각된다. 여기를 자극하면 체성운동계 및 자율계에 넓은 범위로 영향을 미치고, 식욕 ·성욕 등의 욕구행동에 일련의 영향을 나타낸다.
뇌에서 감정을 담당하는 부위는 1937년 파페츠(Papez) 가 대뇌 외측뇌실(lateral ventricle) 주위에 있는 피질구조 와 시상하부(hypothalamus), 그리고 시상(thalamus)을 연결하는 회로 ("파페츠회로 Papez circuit") 에 있다고 주장한 이 후, 이들 구조들과 서로 밀접하게 연결되어 있는 편도체(amygdala), 중격부(septal region), 시상하부(hypothalamus) 등과 함께 변연계(limbic system) 라고 불리워진다.
변연계(邊緣系, limbic system)는 대뇌피질과 간뇌 사이의 경계에 위치한 부위로, 겉에서 보았을 때 귀 바로 위쪽(또는 측두엽의 안쪽)에 존재한다. 감정, 행동, 동기부여, 기억, 후각 등의 여러 가지 기능을 담당한다. 대뇌변연계, 둘레계통이라고도 한다.
변연계라는 개념은 정신의학, 신경학에서 사용되고 있지만 그 정확한 기능과 정의는 계속 변화되고 있다.
이름의 유래
변연계(limbic system)는 1952년에 의사이자 신경과학자인 폴 D. 매클린에 의해서 처음 도입된 단어이다. 다만 브로카 영역의 폴 브로카는 1878년에 뇌의 이 부위를 "le grand lobe limbique" 라고 처음으로 불렀다.
"limbic"은 경계, 가장자리를 뜻하는 라틴어인 limbus에서 따온 말로, 특히 의학에서는 해부학적인 구조의 경계를 뜻한다. 브로카는 기능적으로 다른 뇌 내의 두 구조 사이에 낀 물리적인 위치를 지칭할 때 이 용어를 사용하려고 만들었다.
구조
변연계는 변연엽과 그 안에 해마와 그와 연결된 조직들로 이루어져 있다.
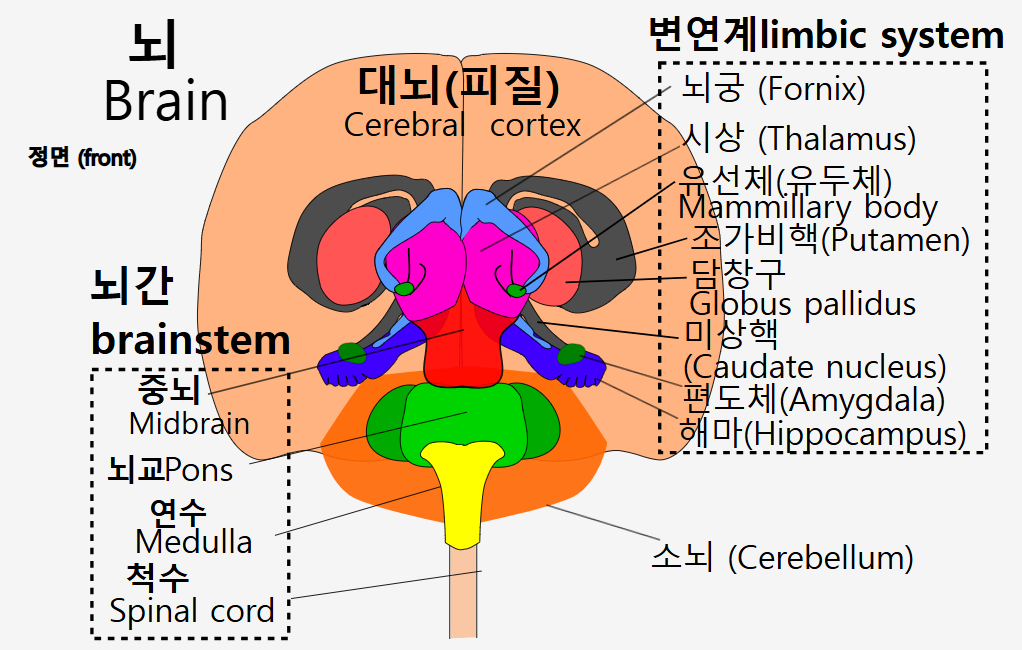
특히 꼬리핵(미상체)와 조가비핵을 함께 아울러 선조체(striatum)라고도 한다. 이 선조체 꼬리와 해마체(hippocampus)의 머리영역(치상회)이 만나는 영역에 편도체(amygdala)가 놓여서 위치하고 있다. 한편 담창구(globus pallidus)는 조가비핵(putamen)과 시상(thalamus)사이에 끼여있는 영역에 위치하는 구형(ball)의 신경다발 덩어리이다. 아직까지 유두체(mammillary body,MB)의 주요기능은 시상과 담창구 그리고 선조체로 이어지는 경로의 메커니즘에서 잘 알려지지 않았지만 해마와 뇌량대상피질(retrosplenial(cingulate)cortex) 신경세포 다발이 뇌궁의 그것에서 처럼 유두체와 관련있다는 연구결과가 있다.
변연엽(limbic lobe)
해마곁이랑(parahippocampal gyrus): 공간기억을 형성하는 역할
띠이랑(또는 대상회,cingulate gyrus): 심박수, 혈압을 조절하는 자율신경기능, 인지적 과정, 주의집중과정에 관여
치아이랑(치상회(DG),dentate gyrus):이빨모양의 형태로 새로운 기억의 형성에 관여한다고 연구 및 보고되고있다. 해마 줄기를 형성하게 되는 연합뉴런(inter-neuron)들과 과립세포(granule cells ,GC)들의 신경다발은 해마를 드나드는 모든 정보들이 예외없이 이곳을 거치게 되는 곳이다.
뇌들보밑이랑(subcallosal gyrus) : 뇌량하부
※ 덧붙여 아래의 구조들도 때에 따라 변연계의 일부로 여겨지기도 한다.
내후각피질(entorhinal cortex): 기억과 관련
조롱박피질(piriform cortex): 후각과 관련된 기능
뇌활이랑(fornicate gyrus): 띠이랑, 해마곁이랑을 합쳐서 뇌활이랑이라고도 한다.
측좌핵(nucleus accumbus): 보상, 기쁨, 중독과 관련
안와전두엽피질(orbitofrontal cortex): 의사결정과 관련된 구조
해마와 그와 연결된 조직들
해마(hippocampus): 뿔처럼 곡선으로 생긴 2개의 조직으로 그 끝에 편도체가 있다. 인지능력과 관련이 깊고 장기기억형성, 공간지각을 위해 필요한 조직이다. 해마가 손상되면 손상되기 전의 기억은 그대로 유지하지만 손상된 후에는 새로운 기억을 생성할 수 없다.
편도체(amygdala): 보상과 공포, 그리고 짝짓기와 같은 사회적 기능과 관련 있는 구조로 2개의 아몬드 모양의 신경 집합체이다. 편도체는 해마를 자극하여 환경을 둘러싼 여러 세부사항을 기억하게 한다.
뇌활(뇌궁): 해마에서 유두체와 사이막핵(septal nuclei)으로 신호를 전달해주는 C자 모양의 축삭돌기 다발.
유두체 또는 유선체(mammillary body): 뇌활의 앞쪽 끝에 있으며 인지기억(recognition memory)과 관련이 있다.
사이막핵(septal nuclei): 뇌량(corpus callsum)의 아래쪽에 있으며, 후각신경구, 해마, 편도체, 시상하부, 시상 등에서 오는 상호 신호를 받는 부위이다. 후각과는 관련이 없으며 보상과 관련된 중요한 역할을 한다.
후각신경구(olfactory bulbs)
시상앞핵(anterior thalamic nuclei)
고삐교차연결(habenular commissure)
The limbic system
The limbic system is the part of the brain involved in our behavioural and emotional responses, especially when it comes to behaviours we need for survival: feeding, reproduction and caring for our young, and fight or flight responses.
You can find the structures of the limbic system buried deep within the brain, underneath the cerebral cortex and above the brainstem. The thalamus, hypothalamus (production of important hormones and regulation of thirst, hunger, mood etc) and basal ganglia (reward processing, habit formation, movement and learning) are also involved in the actions of the limbic system, but two of the major structures are the hippocampus and the amygdala.
Hippocampus
The hippocampus, like many other structures in the brain, comes as a pair, one in each hemisphere of the brain. It resembles the shape of a curvy seahorse (and is named after its scientific genus) and is essentially the memory centre of our brains. Here, our episodic memories are formed and catalogued to be filed away in long-term storage across other parts of the cerebral cortex.
Connections made in the hippocampus also help us associate memories with various senses (the association between Christmas and the scent of gingerbread would be forged here). The hippocampus is also important for spatial orientation and our ability to navigate the world.
The hippocampus is one site in the brain where new neurons are made from adult stem cells. This process is called neurogenesis, and is the basis of one type of brain plasticity. So it’s not surprising this is a key brain structure for learning new things.
Amygdala
The amygdala’s name refers to its almond-like shape. Located right next to the hippocampus, the left and right amygdalae play a central role in our emotional responses, including feelings like pleasure, fear, anxiety and anger. The amygdala also attaches emotional content to our memories, and so plays an important role in determining how robustly those memories are stored. Memories that have strong emotional meaning tend to stick.
The amygdala doesn't just modify the strength and emotional content of memories; it also plays a key role in forming new memories specifically related to fear. Fearful memories are able to be formed after only a few repetitions. This makes ‘fear learning’ a popular way to investigate the mechanisms of memory formation, consolidation and recall.
QBI researchers are working on mapping the neural connections that underpin learning and memory formation in the amygdala. Suppressing or stimulating activity in the amygdala can influence the body’s automatic fear response, which kicks in when something unpleasant happens, such as a startling noise. Through this research, QBI scientists have identified receptors in the amygdala that could help to develop new types of anti-anxiety drugs.
Recently QBI researchers have confirmed that new neurons are made in the amygdala.