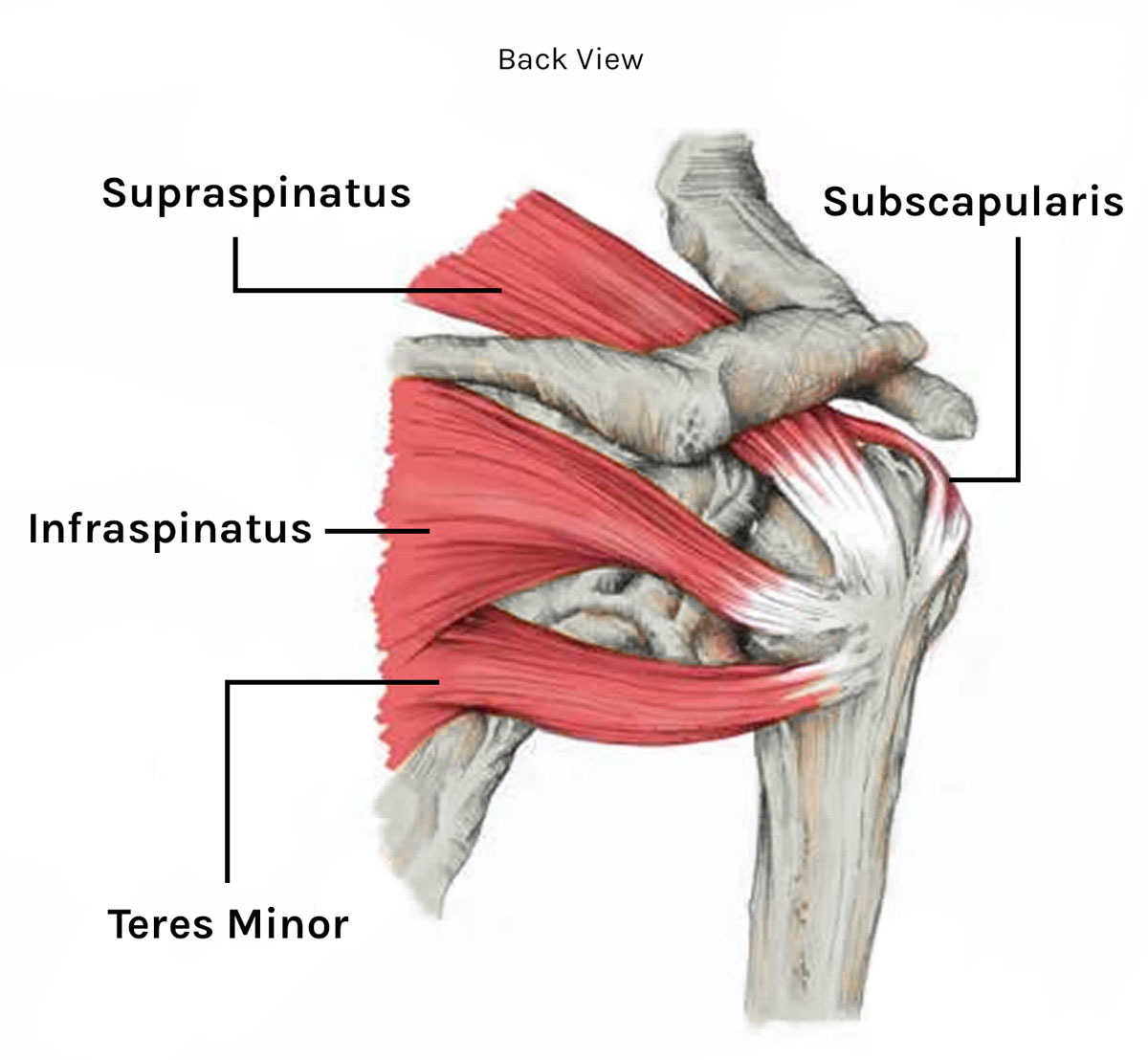
회전근개(rotator cuff), 돌림근띠
어깨 관절을 안정시키기 위한 근육과 힘줄의 조합을 말한다. 이는 7개의 어깨위팔근육(scapulohumeral muscle) 중에 가시위근(supraspinatus), 가시아래근(infraspinatus) 작은원근(teres minor), 어깨밑근(subscapularis) 총 4개의 근육으로 이루어져 있다.
회전근개(Rotator cuff)를 이루는 근육
| 근육 | 기시부 | 종지부 | 기능 | 신경지배 |
| 극상근(supraspinatus) | 견갑골의 극상와 | 상완골의 대결절 | 상완골의 외전 | Suprascapular nerve(C5) |
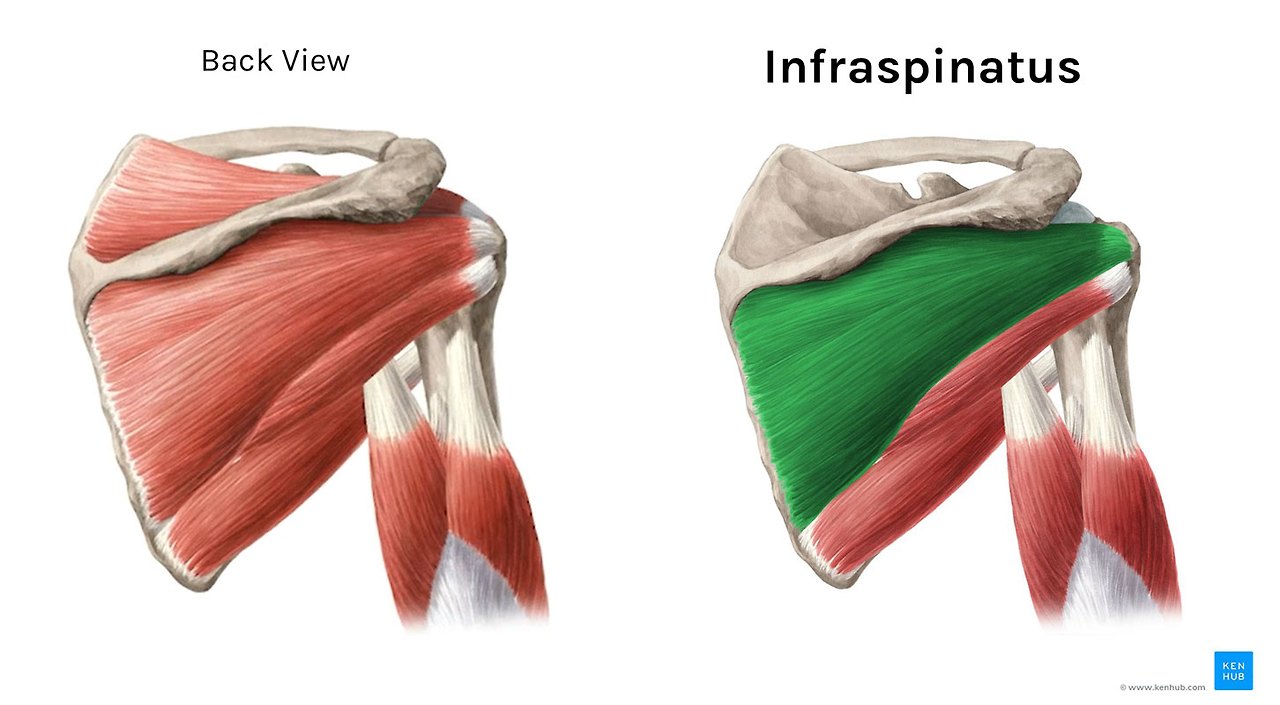
| 극하근(infraspinatus) | 견갑골의 극하, 내측 | 상완골의 대결절 | 상완골의 외측회전 | Suprascapular nerve(C5, 6) |
| 소원근(teres minor) | 견갑골의 극하, 외측 | 상완골 대결절 | 상완골의 내전, 외측회전 | Axillary nerve(C5) |
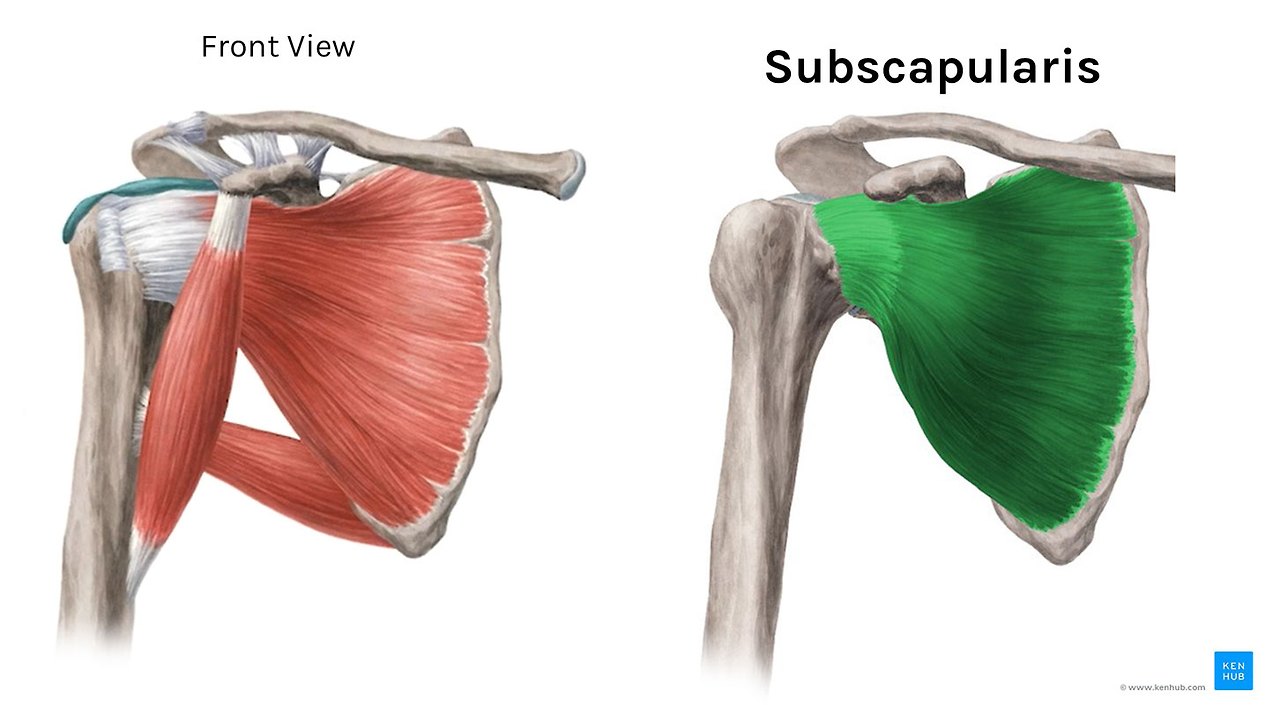
| 견갑하근(subscapularis) | 견갑골의 전면 | 상완골 소결절 | 상완골의 내측회전 | Upper, lower subscapular nerve(C5, C6) |
기능
회전근개는 어깨관절의 움직임과 결합 안정성을 유지하는 데 중요한 구조이다. 4개의 근육이 견갑골에서 기시하여 상완골두에 종지하여 어깨에 둥근 테두리 형태를 형성한다. 이것이 상완골을 견갑골의 작고 얕은 견갑와에 부착되게 한다.
팔의 외전운동 시, 상완골은 관절부로부터 멀어지는 운동을 하게 되며, 이 때 회전근개가 어깨관절을 붙잡는 작용을 한다. 이 작용으로 인해 삼각근의 팔을 들어올리는 동작이 잘 일어날 수 있다. 만약 회전근개가 없을 경우에는 상완골두가 견갑와를 벗어나 위로 치우치므로 삼각근의 동작이 약화된다. 견갑와의 전-후 방향은 깊이가 상-하 방향보다 얕으므로 외력에 약하다. 회전근개의 고정 작용과 안정성은 관절에 작용하는 힘의 세기와 방향에 따라 달라진다.
어깨관절의 안정화 외에도 회내근개는 어깨근육의 내전, 내측회전, 외측회전 등을 수행한다. 극하근과 견갑하근은 극상근보다 2~3배 강한 힘을 만들어내어 어깨의 외전에 중요한 역할을 한다. 다만 효율은 극상근보다 낮기 때문에, 외전에는 극상근이 주동근 역할을 한다.
임상적 중요성
근육 파열(Tear). 일반적으로 극상근(supraspinatus)이 손상됨.
1. 근육파열(Tear)
회전근개 근육의 끝지점의 힘줄(tendon)이 찢어질 수 있어 팔에 통증을 느끼게 되고 움직이지 못하게 된다. 찢어진 회전근개 근육은 어깨를 움직이지 못하도록 하거나, 힘줄에 마모가 생기게 하는데, 아크로미온 아래에 있는 극상근(supraspinatus) 근육의 힘줄이 가장 일반적으로 마모가 생긴다.
2. 어깨 충돌 증후군(Impingement Syndrome)
회전근개 근육의 어깨 부위의 통증은 건병증(tendinosis)으로 인해 흔하게 나타난다. 건병증은 나이와 관련이 있고, 힘줄이 손상되었을 경우 치유되는 시간을 주지 못한 채 힘줄의 과사용이 지속되는 경우에 발생한다.
The Rotator Cuff
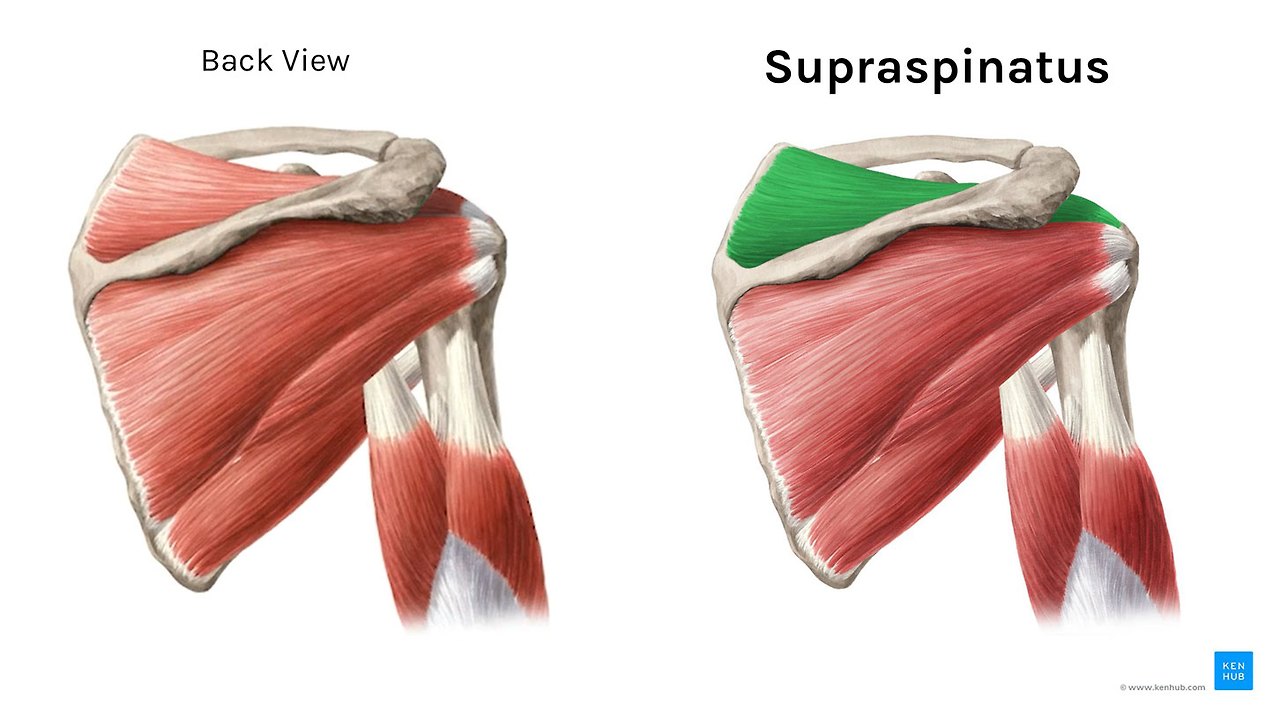
Supraspinatus is above-the spine of your shoulder blade and is the topmost rotator cuff muscle. It helps the Deltoid lift the arm up & away from the body (abduction).
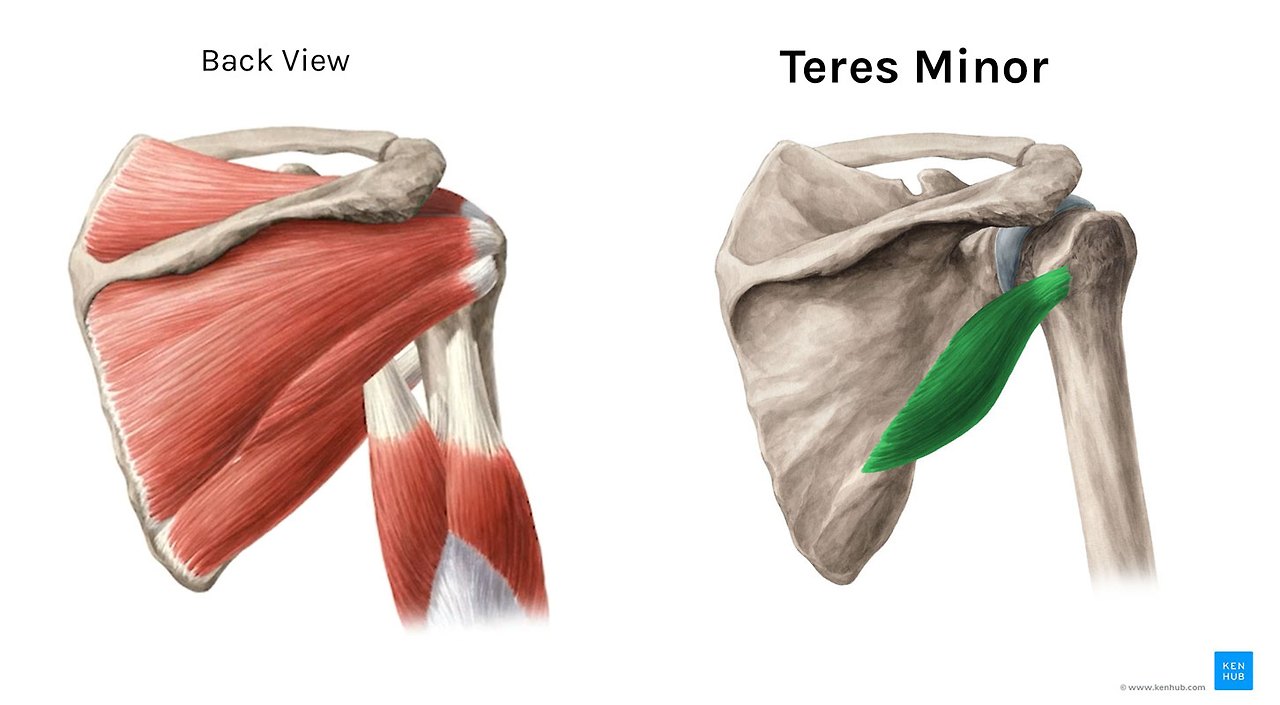
Teres Minor is a small, narrow muscle which sits just underneath the Infraspinatus and attaches to the humerus slightly lower. It’s main job is external rotation alongside the Infraspinatus, but, because of it’s slightly different position it’s more active when your arm is lifted (abducted) over 90 degrees.
They’re so commonly grouped together because even though they all have their own main task, it’s very difficult to completely separate their actions. These four muscles work together every time you move your shoulder, both creating movement and by reducing unwanted/unexpected wobbles.
