유성기어 장치
유성기어 장치란 일정 회전비를 통해 고정축 주위를 회전하는 일반 기어와 달리 태양기어 주위에 있는 유성기어를 캐리어로 지지해 회전하는 기어열이다.
이 때 태양기어는 자전운동을 수행하는 반면에 유성기어는 자전과 공전운동을 하는데, 캐리어 역시 유성기어처럼 공전운동을 실행한다. 한편, 유성기어장치라는 이름은 태양을 중심으로 자전과 공전 운동을 하는 태양계 구조와 유사하다고 하여 붙여진 이름인데, 유성치차감속기라는 또 다른 이름이 쓰이기도 한다.
유성기어 장치의 특성
장점
유성기어장치는 소형 크기임에도 불구하고 큰 동력 전달 비율을 통해 일반 기어 감속기보다 더 큰 동력을 전달한다.
또한 유성기어장치는 입·출력축을 동심으로 수행하며, 각 기어가 담당하는 전달 하중과 속도를 줄여 마찰 손실은 줄이고, 동력 전달 효율은 상승시킨다.
이외에도 유성기어장치는 다수의 치차를 접촉시켜 고토크와 고강도를 구현하며, 태양기어와 3개의 유성기어를 맞물리게 해 부하가 정확히 3등분으로 분산되게 하는데, 이는 내구성 향상에 긍정적인 영향을 미친다.
단점
위와 같은 장점에도 불구하고 유성기어장치는 내부에 있는 유성기어가 공전운동을 하면서 발생시키는 원심력 때문에 고속 사용 시 사용자가 각별한 주의를 기울여야만 하는 단점을 가지고 있다.
게다가 유성기어장치는 많은 구성 부품으로 이뤄져 있어 작은 전달 동력이 전달됐을 때 일반 변속기어보다 더 많은 비용을 발생시키기도 한다.
또한 유성기어장치가 충분한 성능을 발휘하도록 하려면, 설계 및 제작 단계에서 고도의 기술을 적용해야 하는데, 이 역시 유성기어장치의 단점으로 꼽힌다.
백래시, Backlash
Backlash란 기어가 서로 맞물릴 때 원주 방향으로 이와 이 사이가 벌어져 생기는 틈새를 의미하는 용어이다.
기어 이빨이 밀접하게 붙어 있으면, 회전저항과 과도한 마모가 발생하는 반면에 너무 떨어져 있을 시에는 유격이 발생해 정확한 제어가 불가능하고, 기어 끝부분이 조기 마모 현상을 겪게 된다.
기어쌍이 반대 방향으로 토크를 받지 않는 이상 Backlash는 문제가 되지 않는다. 하지만 토크의 방향이 바뀔 때마다 이가 접촉하는 부분이 바뀌게 되고, Backlash 간격이 좌우로 움직이면서 이가 소음을 내는 동시에 충격을 발생시킨다.
또한 Backlash는 응력과 마모를 증가시킬 뿐만 아니라 몇몇 응용 분야에서는 위치 오차를 일으키기도 한다.
Backlash의 단위
Backlash의 단위에는 arcmin과 srcsec이 있는데, 1arcmin의 경우, 60분의 1도로, 약 0.016도인 반면, 1srcsec은 360분의 1도로, 약 0.000277도이다.
한편, 감속기의 정밀도를 나타내는 값으로 Backlash를 보편적으로 쓰는데, 이외에 감속기의 입력축을 고정시킨 상태에서 출력축을 정해진 토크로 회전시켰을 때 도출되는 값으로 감속기 정밀도를 명시하는 경우도 있다.
이러한 현상은 감속기 정밀도를 나타내는 기준이 제조사마다 상이하다는 것을 나타낸다.
A planetary gear set
also known as an epicyclic gear train, is a compact gear assembly that can increase or decrease speed and torque. It's made up of three main gears: a sun gear, planet gears, and a ring gear.
| Gear | Description |
| Sun gear | The central gear that acts as the input gear |
| Planet gears | The driven gears that rotate around the sun gear |
| Ring gear | The internal spur gear that the planet gears engage with |
Planetary gear sets are used in: automotive and off-road transmissions, wheel drives, industrial conveyors, and automatic transmissions.
How planetary gear sets work
The planet gears are mounted on a carrier that rotates, carrying the planet gears around the sun gear. The planet and sun gears mesh so that their pitch circles roll without slip.
Advantages of planetary gear sets
Planetary gear sets are compact, efficient, and low noise. They're also robust and adaptable to various gear ratios.
Applications
Planetary gear sets can vary in complexity from very simple to intricate compound systems, depending on the application.
유성기어는 그림 1과 같이 중심에 태양과 같이 자전을 하는 썬기어 (sun gear), 썬기어 주위를 행성처럼 회전하는 planet gear, 그리고 최외곽에 링기어로 구성되어 있습니다. 또한 planet gear를 일체형으로 움직이게 하는 캐리어 (carrier)가 있습니다.

그림. 1 유성기어의 구조
유
성기어의 구속조건을 살펴보면 다음과 같습니다. 그림 1을 참고하면 링기어의 지름은 캐리어의 지름과 planet 기어 지름의 합과 같습니다.

식. 1
또한, 캐리어의 지름은 썬기어와 planet 기어 지름의 합과 같습니다.

식. 2
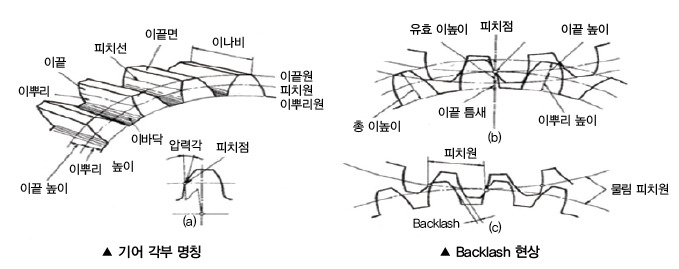
식 1의 P에 식 2를 대입하여 정리하면 식 3과 같습니다.
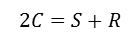
식. 3
이제 기어비에 의해 각 기어의 이빨 수와 회전 수를 곱하면 식 4와 같은 등식을 얻어낼 수 있습니다.


식. 4
썬기어, 링기어, 캐리어 중 한개는 입력, 한개는 기어비를 통과한 출력, 한개는 하우징과 고정되는 역할을 합니다. 아래 표와 같이 3가지 경우로 많이 쓰이는데 각각 경우에 따라 기어비가 어떻게 달라지는지 살펴보겠습니다.

Case 1
case 1은 링기어가 고정이기 때문에 링기어의 회전수 항을 0으로 두면 썬기어가 입력 캐리어가 출력인 경우로 사용합니다. 따라서 썬기어에서 부터 캐리어까지의 기어비는 식 5와 같습니다.

식. 5
이를 레버선도로 표현하면 아래 그림과 같습니다. 링기어와 썬기어의 비를 삼각비를 통해 회전수 비로 나타낼 수 있는 것입니다. 썬기어 회전수에 대한 밑변 길이가 R+S이고 캐리어에 대한 밑변의 길이가 S이므로 삼각비가 식 5와 일치하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
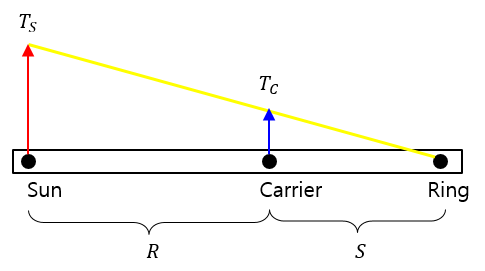
Case 2
case 2는 썬기어가 고정이기 때문에 썬기어의 회전수 항을 0으로 두면 캐리어가 입력 링기어가 출력인 경우로 사용합니다. 따라서 캐리어에서 부터 링기어까지의 기어비는 식 6과 같습니다.

식. 6
Case 1과 마찬가지로 레버선도 표현하면 아래와 같습니다.
Case 3
case 3은 캐리어가 고정이기 때문에 캐리어의 회전수 항을 0으로 두면 썬기어가 입력 링기어가 출력인 경우로 사용합니다. 따라서 썬기어에서 부터 링기어까지의 기어비는 식 7과 같습니다. 여기서 캐리어 3쌍이 묶인채로 고정된다는 것이고, 캐리어는 개별적으로 제자리에서 돌고 있습니다.

식. 7
식 7은 음의 부호이기 때문에 썬기어와 링기어의 회전 방향이 반대라는것을 알 수 있습니다. 이를 레버선도표 표현하면 캐리어가 고정일 때는 썬기어와 링기어의 방향이 반대인것을 확인할 수 있습니다.

An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) is a gear reduction assembly consisting of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear (the "planet") revolves around the center of the other (the "sun"). A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates, to carry the planet gear(s) around the sun gear. The planet and sun gears mesh so that their pitch circles roll without slip. If the sun gear is held fixed, then a point on the pitch circle of the planet gear traces an epicycloid curve.
An epicyclic gear train can be assembled so the planet gear rolls on the inside of the pitch circle of an outer gear ring, or ring gear, sometimes called an annulus gear. Such an assembly of a planet engaging both a sun gear and a ring gear is called a planetary gear train.12 By choosing to hold one component or another—the planetary carrier, the ring gear, or the sun gear—stationary, three different gear ratios can be realized.3
Overview
The red marks show the relative displacement of the sun gear and carrier, when the sun gear is rotated 180° clockwise and the ring gear is held fixed.
Epicyclic gearing or planetary gearing is a gear system consisting of one or more outer, or planet, gears or pinions, revolving about a central sun gear or sun wheel.45 Typically, the planet gears are mounted on a movable arm or carrier, which itself may rotate relative to the sun gear. Epicyclic gearing systems also incorporate the use of an outer ring gear or annulus, which meshes with the planet gears. Planetary gears (or epicyclic gears) are typically classified as simple or compound planetary gears. Simple planetary gears have one sun, one ring, one carrier, and one planet set. Compound planetary gears involve one or more of the following three types of structures: meshed-planet (there are at least two more planets in mesh with each other in each planet train), stepped-planet (there exists a shaft connection between two planets in each planet train), and multi-stage structures (the system contains two or more planet sets). Compared to simple planetary gears, compound planetary gears have the advantages of larger reduction ratio, higher torque-to-weight ratio, and more flexible configurations.6
The axes of all gears are usually parallel, but for special cases like pencil sharpeners and differentials, they can be placed at an angle, introducing elements of bevel gear (see below). Further, the sun, planet carrier and ring axes are usually coaxial.
Bookwheel, from Agostino Ramelli's Le diverse et artifiose machine, 1588
Epicyclic gearing is also available which consists of a sun, a carrier, and two planets which mesh with each other. One planet meshes with the sun gear, while the second planet meshes with the ring gear. For this case, when the carrier is fixed, the ring gear rotates in the same direction as the sun gear, thus providing a reversal in direction compared to standard epicyclic gearing.
History
Around 500 BC, the Greeks invented the idea of epicycles, of circles travelling on the circular orbits. With this theory Claudius Ptolemy in the Almagest in 148 AD was able to approximate planetary paths observed crossing the sky. The Antikythera Mechanism, circa 80 BC, had gearing which was able to closely match the Moon's elliptical path through the heavens, and even to correct for the nine-year precession of that path.7 (The Greeks interpreted the motion they saw, not as elliptical, but rather as epicyclic motion.)
In the 2nd century AD treatise The Mathematical Syntaxis (a.k.a. Almagest), Claudius Ptolemy used rotating deferent and epicycles that form epicyclic gear trains to predict the motions of the planets. Accurate predictions of the movement of the Sun, Moon, and the five planets, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn, across the sky assumed that each followed a trajectory traced by a point on the planet gear of an epicyclic gear train. This curve is called an epitrochoid.citation needed
Epicyclic gearing was used in the Antikythera Mechanism, circa 80 BC, to adjust the displayed position of the Moon for the ellipticity of its orbit, and even for its orbital apsidal precession. Two facing gears were rotated around slightly different centers; one drove the other, not with meshed teeth but with a pin inserted into a slot on the second. As the slot drove the second gear, the radius of driving would change, thus invoking a speeding up and slowing down of the driven gear in each revolution.citation needed
Richard of Wallingford, an English abbot of St. Albans monastery, later described epicyclic gearing for an astronomical clock in the 14th century.8 In 1588, Italian military engineer Agostino Ramelli invented the bookwheel, a vertically revolving bookstand containing epicyclic gearing with two levels of planetary gears to maintain proper orientation of the books.89
French mathematician and engineer Desargues designed and constructed the first mill with epicycloidal teeth c. 1650.10